In today's digital age, intellectual property (IP) is a valuable asset for individuals, businesses, and organizations. Protecting your IP is crucial to prevent unauthorized use, theft, and exploitation. Here, we will explore five ways to protect your IP tech, highlighting the importance of each method and providing practical tips for implementation.
Why IP Protection Matters
Intellectual property protection is essential for several reasons:
- Prevents unauthorized use and theft of your creations
- Safeguards your brand reputation and goodwill
- Enhances your competitive advantage in the market
- Allows you to license and monetize your IP
- Fosters innovation and creativity
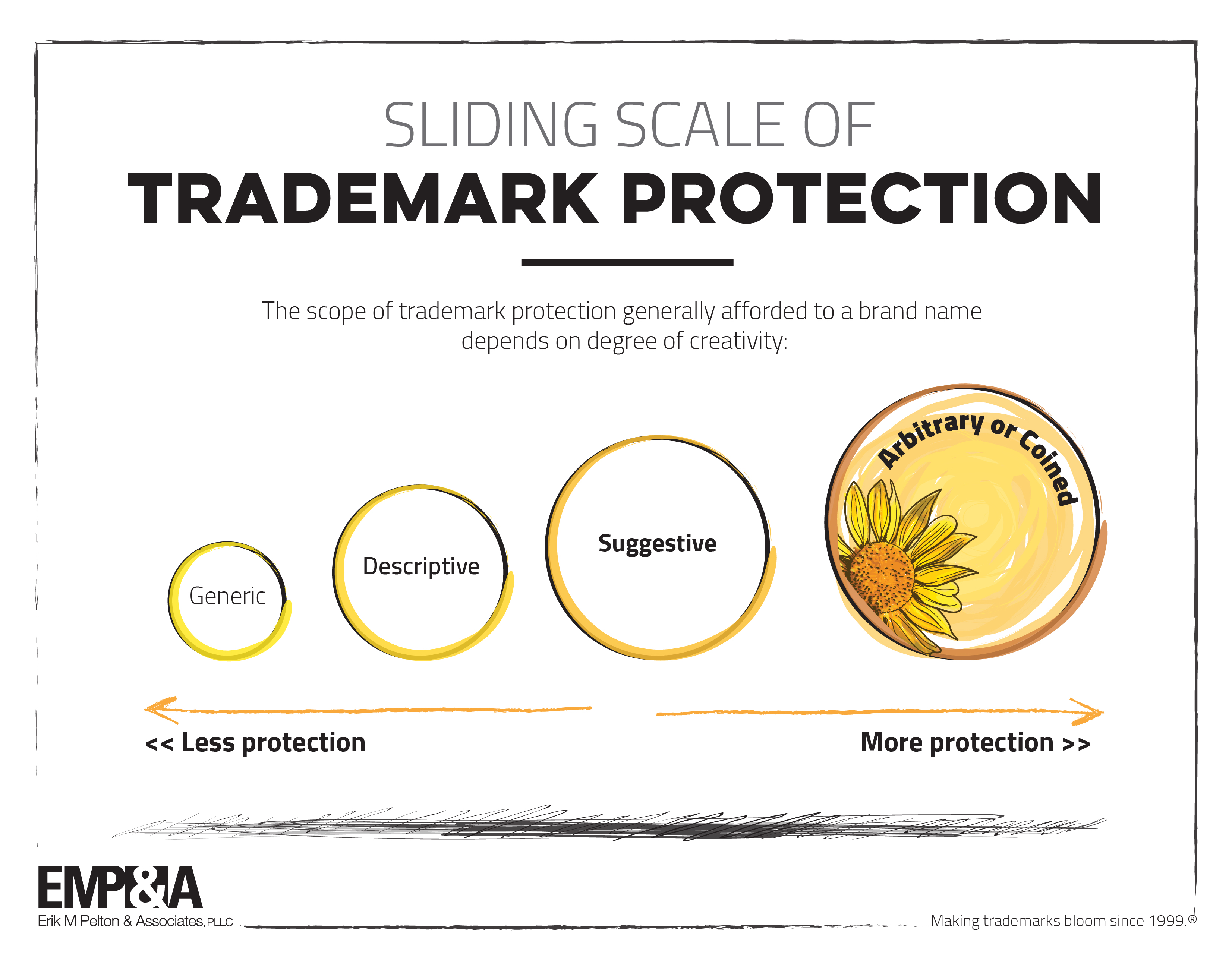
1. Trademark Protection
A trademark is a unique sign, symbol, or phrase that identifies your brand and distinguishes it from others. Registering your trademark provides legal protection and prevents others from using similar marks.
- Conduct a trademark search: Ensure your desired mark is available and doesn't infringe on existing trademarks.
- File a trademark application: Submit your application to the relevant intellectual property office, providing detailed descriptions and examples of your mark.
- Maintain your trademark registration: Pay renewal fees and update your registration as necessary to keep your trademark protected.
2. Patent Protection
A patent is a government-granted monopoly that protects your inventions and innovations. Patent protection prevents others from making, using, or selling your invention without permission.
- Determine the type of patent: Decide whether you need a utility patent, design patent, or plant patent, depending on your invention.
- Conduct a patent search: Ensure your invention is novel and non-obvious by searching existing patents and prior art.
- File a patent application: Submit your application, including detailed descriptions, drawings, and claims.

3. Copyright Protection
Copyright protects your original literary, dramatic, musical, and artistic works, including software code and digital content. Registering your copyright provides a public record of your ownership.
- Create original work: Ensure your work is unique and not copied from others.
- Register your copyright: File your application with the relevant copyright office, providing a copy of your work.
- Use copyright notices: Display the copyright symbol, your name, and the year of publication to deter infringement.

4. Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs)
NDAs are contracts that protect confidential information, such as trade secrets and business strategies. NDAs prevent unauthorized disclosure and use of sensitive information.
- Identify confidential information: Determine what information needs protection and limit access to authorized personnel.
- Draft an NDA: Create a contract that outlines the terms of confidentiality, including the consequences of breach.
- Use NDAs with partners and employees: Ensure all parties who access confidential information sign an NDA.

5. Trade Secret Protection
Trade secrets are confidential information that provides a competitive advantage. Protecting trade secrets involves limiting access and using security measures.
- Identify trade secrets: Determine what information is critical to your business and needs protection.
- Limit access: Restrict access to authorized personnel and use secure storage and transmission methods.
- Use security measures: Implement encryption, passwords, and other security measures to protect digital trade secrets.

By implementing these five methods, you can effectively protect your IP tech and safeguard your creative and innovative work.
Gallery of IP Protection





FAQs
What is intellectual property protection?
+Intellectual property protection refers to the legal measures used to safeguard creative and innovative work, including trademarks, patents, copyrights, and trade secrets.
Why is IP protection important?
+IP protection prevents unauthorized use and theft, safeguards brand reputation, and enhances competitive advantage.
How can I protect my IP tech?
+You can protect your IP tech by using trademarks, patents, copyrights, non-disclosure agreements, and trade secret protection.
